Roldán et al. 2015, Protoplasma
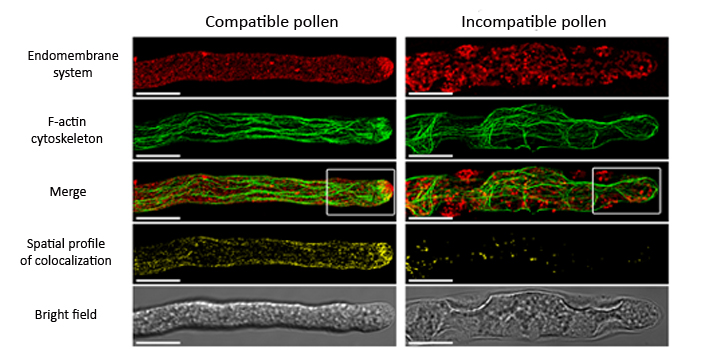
In the S-RNase-based self-incompatibility system, subcellular events occurring in the apical region of incompatible pollen tubes during the pollen rejection process are poorly understood. F-actin dynamics and endomembrane trafficking are crucial for polar growth, which is temporally and spatially controlled in the tip region of pollen tubes. Thus, we developed a simple in vitro assay to study the changes in the F-actin cytoskeleton and the endomembrane system at the apical region of incompatible pollen tubes in Nicotiana alata. Growth but not germination of pollen tubes of S c₁₀-, S₇₀-, and S₇₅-haplotypes was selectively inhibited by style extracts carrying the same haplotypes. Pollen F-actin cytoskeleton and endomembrane system, visualized by fluorescent markers, were normal during the initial 60 min of pollen culture in the presence of compatible and incompatible style extracts. Additional culture resulted in complete growth arrest and critical alterations in the integrity of the F-actin cytoskeleton and the endomembrane system of incompatible pollen tubes. The F-actin ring and the V-shaped zone disappeared from the apical region, while distorted F-actin cables and progressive formation of membrane aggregates evolved in the subapical region and the shank. The vacuolar network of incompatible pollen tubes invaded the tip region, but vacuolar membrane integrity remained mostly unaffected. The polar growth machinery of incompatible pollen tubes was uncoupled, as evidenced by the severe disruption of colocalization between the F-actin cytoskeleton and the endomembrane compartments. A model of pollen rejection integrating the main subcellular events occurring in incompatible pollen is discussed.
Autores: Roldán JA, Rojas HJ, Goldraij A.
Artículo: Roldán et al, Protoplasma, 2015 Jan;252(1):63-75. doi: 10.1007/s00709-014-0658-4.